How to Fix the True Causes of Dry Skin

How to Fix the True Causes of Dry Skin
Dry skin, or xerosis, is more than a cosmetic concern—it’s often a sign of deeper imbalances within the body. While topical moisturizers offer temporary relief, addressing the root causes holistically can lead to lasting skin health. Let’s explore the hidden triggers and what you need to do to heal your skin from the inside out.
The Hidden Causes
Nutritional Deficiencies
- Insufficient Omega-3 Fatty Acids: these fats strengthen the skin's lipid barrier. Low levels lead to dryness [1].
- Insufficient Vitamins A, E, Zinc: deficiencies, which are common with the standard American diet, cause flaky, rough skin [2,3].
Dehydration
- Inadequate water intake impairs skin elasticity and barrier function, exacerbating dryness [4].
Gut Health Imbalances
- Dysbiosis, or gut microbiome disruption, triggers systemic inflammation, contributing to dry, irritated skin [5].
Hormonal Fluctuations
- Hypothyroidism slows sebum production, while menopause reduces estrogen, both drying skin [6].
- Elevated cortisol and poor sleep disrupt skin repair, leading to dehydration and dullness [7].
Toxins
- Pollutants, harsh soaps, and drugs like diuretics strip natural oils, worsening dryness [8].

Healing Strategies
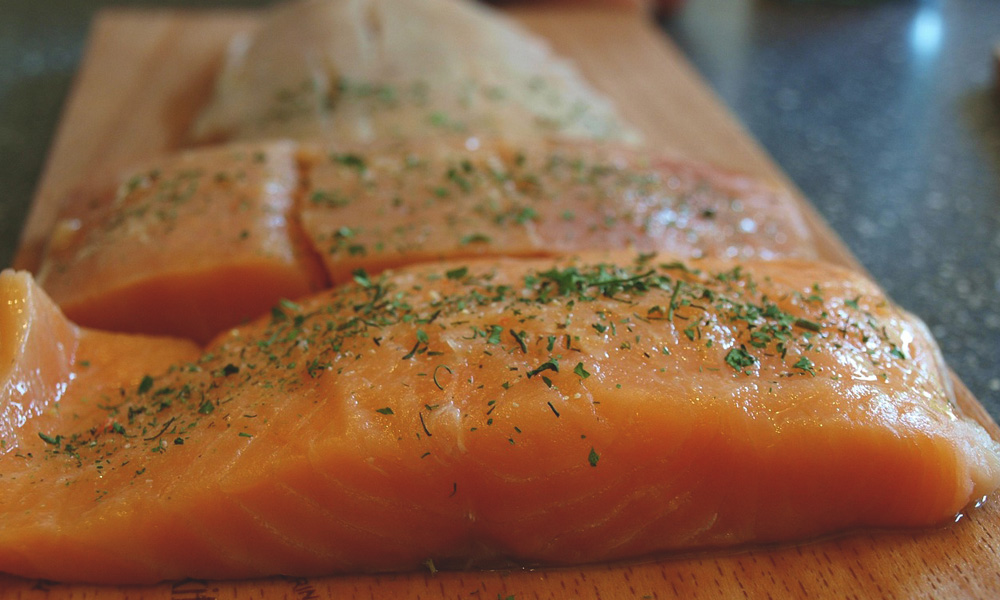

Eat for Skin Health
Eat omega-3-rich foods (wild-caught salmon, grass-fed beef & organs, eggs) to strengthen the skin barrier [1].
Add antioxidants from foods such as berries and sweet potatoes to combat oxidative stress [9].
Incorporate collagen (bone broth and marrow) to support skin elasticity [10].

Hydrate Intentionally
Aim for 2–3 liters of water daily, adjusted for activity and climate [11].
Boost absorption with electrolytes (salt, supplements, fruits).
Sip herbal teas like chamomile, which hydrate and soothe inflammation [12].
Limit dehydrating beverages like alcohol and coffee to prevent moisture loss [4].
Heal Your Gut
- Eliminate processed foods and synthetic ingredients, such as artificial sweeteners and emulsifiers, which damage the gut lining and promote inflammation [13].
- Incorporate fermented foods like kefir or sauerkraut to promote gut health, reducing inflammation [5].
- Eat prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and bananas to feed healthy gut flora [5].
Balance Hormones Naturally
- Get 8 hours of sleep and manage stress with mindfulness practices like yoga to lower cortisol, which damages skin barriers [16].
- Support thyroid function with iodine from seafood, eggs and meat [17].
- Get sunlight exposure (10–30 minutes daily, depending on skin type) to boost vitamin D, which supports thyroid function and skin health [18].
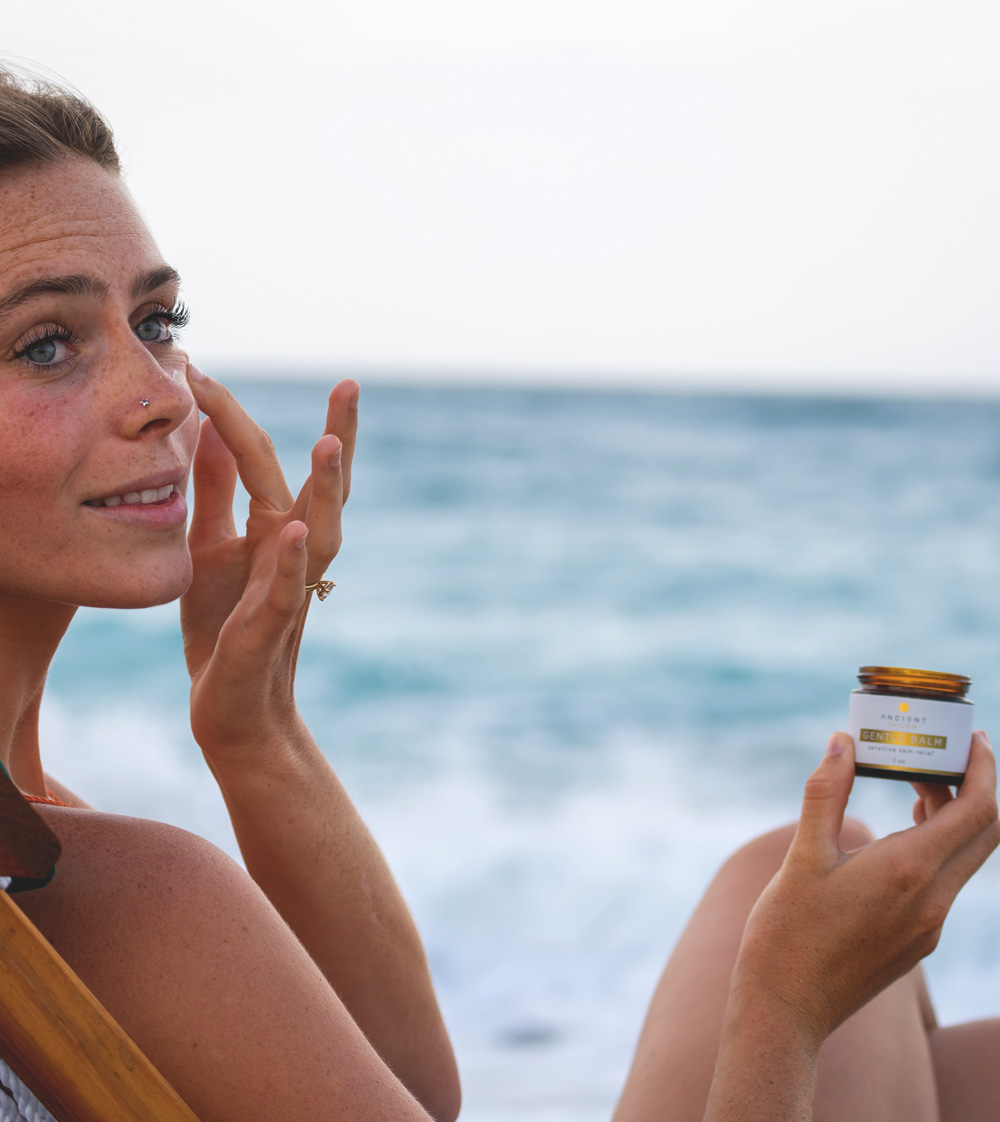

Skincare & Environment
Use tallow-based skincare, derived from grass-fed beef fat, rich in vitamins A, D, E, and K. Its composition closely mimics human sebum, making it highly effective for protecting, hydrating and repairing dry skin [20].
Engage in moderate exercise, like walking or yoga, to boost circulation and deliver nutrients to the skin. Cleanse gently after sweating to prevent dehydration and clogged pores [21].
Avoid hot showers, which strip oils, and use lukewarm water [8].
Filter tap water to remove chlorine and use a humidifier in dry climates to maintain skin hydration [22].
The Dry Skin Collection (promote healing with real skin food)
We live in a reductionist world where issues are treated directly and acutely. It’s important to remember that a good arborist treats leave and fruit issues by focusing on the soil not the leaves themselves. Dry skin is a symptom of deeper issues that need to be fixed at their core not with topical treatments alone.
References
- Balić, A., Vlašić, M., & Mokos, M. (2018). Omega-3 versus omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory skin disorders. Marine Drugs, 16(9), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16090306
- Pappas, A., Liakou, A., & Zouboulis, C. C. (2019). Nutrition and skin: Updates and perspectives. Nutrients, 11(5), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051095
- Fulgoni, V. L., Keast, D. R., Bailey, R. L., & Dwyer, J. (2018). Food and nutrient intakes and overall diet quality in the United States: An analysis of NHANES 2011–2016. Nutrients, 10(12), 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121857
- Palma, L., Marques, L. T., Bujan, J., & Rodrigues, L. M. (2015). Dietary water affects human skin hydration and biomechanics. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 8, 413–421. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S86822
- Lee, S. Y., Lee, E., Park, Y. M., & Hong, S. J. (2021). The gut-skin axis in inflammatory skin diseases. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 650893. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.650893
- Safer, J. D. (2016). Thyroid hormone action on skin. Indian Journal of Dermatology, 61(5), 552–558. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5154.190119
- Oyetakin-White, P., Suggs, A., Koo, B., Matsui, M. S., Yarosh, D., Cooper, K. D., & Baron, E. D. (2017). Does poor sleep quality affect skin ageing? Clinical and Experimental Dermatology, 42(1), 27–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.12955
- Elias, P. M., & Wakefield, J. S. (2021). Therapeutic implications of a barrier-based pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 22(3), 305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-021-00595-8
- Petruk, G., Del Giudice, R., Rigano, M. M., & Monti, D. M. (2018). Antioxidants from plants protect against skin photoaging. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2018, 5417165. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5417165
- Choi, F. D., Sung, C. T., Juhasz, M. L., & Mesinkovska, N. A. (2019). Oral collagen supplementation: A systematic review of dermatological applications. Nutrients, 11(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020249
- Pross, N. (2017). Effects of dehydration on brain functioning: A life-span perspective. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 71(8), 990–995. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.79
- Srivastava, J. K., Shankar, E., & Gupta, S. (2010). Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with a bright future. Molecular Medicine Reports, 3(6), 895–901. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2010.377
- Suez, J., Cohen, Y., Valdés-Mas, R., Mor, U., Dori-Bachash, M., Federici, S., … & Elinav, E. (2022). Personalized microbiome-driven effects of non-nutritive sweeteners on human glucose tolerance. Cell, 185(18), 3307–3328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.07.016
- Knackstedt, R., Knackstedt, T., & Gatherwright, J. (2019). The role of topical probiotics in skin conditions. Beneficial Microbes, 10(6), 617–627. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2019.0013
- Drago, L., Arioli, S., Mattina, R., & De Vecchi, E. (2020). Gut microbiota, probiotics, and skin health. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, 54(Suppl 1), S33–S40. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000001414
- Buric, I., Farias, M., Jong, J., Mee, C., & Brazil, I. A. (2018). What is the molecular signature of mind-body interventions? A systematic review of gene expression changes induced by meditation and related practices. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 95, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.008
- Ventura, M., Melo, M., & Carrilho, F. (2017). Selenium and thyroid disease: From pathophysiology to treatment. Thyroid, 27(3), 318–326. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0475
- Holick, M. F. (2017). The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 102(6), 1922–1930. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-00146
- Lephart, E. D. (2020). Skin aging and oxidative stress: Equol’s anti-aging potential. Dermatologic Therapy, 33(6), e14276. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.14276
- Russell, M. F., Sandhu, M., Vail, M., Haran, C., Batool, U., & Leo, J. (2024). Tallow, rendered animal fat, and its biocompatibility with skin: A scoping review. Cureus, 16(5), e60981. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.60981
- Crane, J. D., MacNeil, L. G., Lally, J. S., Ford, R. J., Bujak, A. L., Brar, I. K., … & Tarnopolsky, M. A. (2015). Exercise-stimulated interleukin-15 regulates skin metabolism and aging. Aging Cell, 14(3), 447–456. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12308
- Juliano, C., & Magrini, G. A. (2019). Cosmetic ingredients as emerging pollutants. Environmental Research, 176, 108525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108525
More from the Ancestral Blog

Questions about tallow or your skincare journey?
Sign up for more skincare insights delivered to your inbox!
*Limit once per customer